Cystoid Macular Edama
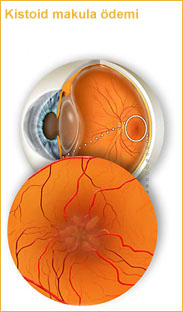
Macular edema is a painless disorder which affects the central retina or macula. When this condition is present, fluid and protein deposits collect on or under the macula of the eye.
Cystoid macular edema is a type of macular edema that includes cyst formation. The swelling may distort a person's central vision, as the macula is near the center of the retina at the back of the eyeball.
CME is a relatively common condition and is frequently associated with various ocular conditions, such as cataract surgery, age-related macular degeneration (ARMD), uveitis, eye injury, diabetes, retinal vein occlusion, or drug toxicity. When CME develops following cataract surgery and its cause is directly related to the surgery.
Although the exact cause of macular edema is not known, it may accompany a variety of diseases such as retinal vein occlusion, uveitis, or diabetes. It most commonly occurs after cataract surgery. About 1-3 % of those who have cataract extractions will experience decreased vision due to CME during the first post-operative year, usually from two to four months after surgery. If the disorder appears in one eye, there is an increased risk as high as 50% that it will also affect the second eye. Fortunately, however, most patients recover their vision with treatment.
Blurred or decreased central vision (the disorder does not affect peripheral or side-vision). Painless retinal inflammation or swelling (usually after cataract surgery). The symptoms described above may not necessarily mean that you have cystoid macular edema. However, if you experience one or more of these symptoms, contact your eye doctor for a complete exam.
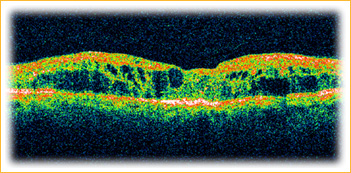
It is very difficult to detect CME during a routine examination. A diagnosis is often based on the patient’s symptoms and a special dye test called a fluorescein angiogram (FA).
The first line of treatment for CME is usually anti-inflammatory drops. In certain cases, medication is injected near the back of the eye for a more concentrated effect. Oral medications are sometimes prescribed to reduce the swelling.
Last Updated: October 23, 2024